Related Categories
Related Articles
Articles
"VIX - CBOE Volatility Index" (May 2015)
INVESTOPEDIA EXPLAINS the 'VIX - CBOE Volatility Index'
The first VIX, introduced by the CBOE in 1993, was a weighted measure of the implied volatility of eight S&P 100 at-the-money put and call options. Ten years later, it expanded to use options based on a broader index, the S&P 500, which allows for a more accurate view of investors' expectations on future market volatility. VIX values greater than 30 are generally associated with a large amount of volatility as a result of investor fear or uncertainty, while values below 20 generally correspond to less stressful, even complacent, times in the markets.
http://www.investopedia.com
the VIX as it is now can be seen in the following chart (as marked the VIX made its lows in the past years around the 10 - 13 level):
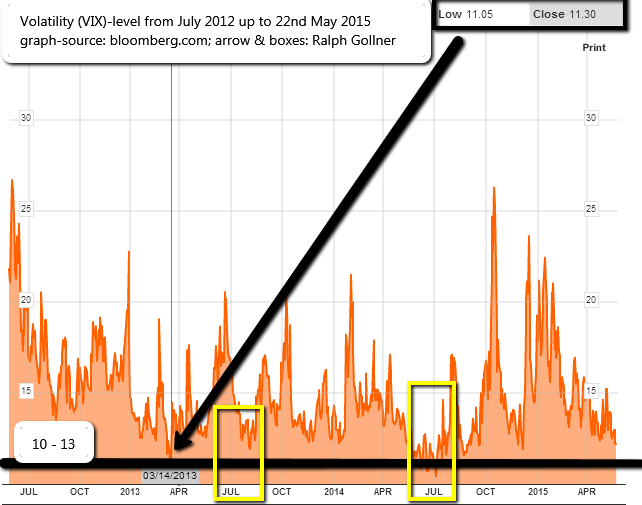 Source: http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/VIX:IND/chart
Source: http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/VIX:IND/chart
final remarks (mainly taken from following site: http://finance.yahoo.com )
The VIX typically moves higher when stocks plunge. Investors would turn to S&P 500 options to protect their portfolios against any sudden dips.
But be careful: Volatility products are designed to “roll” the contracts over periodically to maintain exposure to VIX futures. They can lose money on this trade when longer-dated contracts are more expensive than the front-month contract, or when markets are said to be in “contango.”



