Related Categories
Related Articles
Articles
Diversification (Number of stocks)
Investment theory, and intuition, tell us that risk is reduced by diversification - not putting everything in one basket by holding more than one stock. The question naturally arises: how many stocks should one hold?
What diversification can and cannot do
Before answering the question of how many stocks it takes, we need to note that diversification can only reduce the volatility risk associated with an individual company. It cannot reduce the so-called market or systematic risk common to all stocks, visible as generalized movement up or down in the same direction at the same time. It makes sense that macro-economic factors like booms and recessions and financial crises often drive stocks in the same direction. That is market risk and is not diversifiable. The kind of risk that can be diversified is the non-systematic risk associated with individual companies due to management skill, product success and the like.
The theoretical answer - 15 to 50 stocks
Consult a finance textbook or paper such as How Efficient is Naive Portfolio Diversification? by Gordon Tang of Hong Kong Baptist University and you will find this kind of statement - "for an infinite population of stocks, a portfolio size of 20 is required to eliminate 95% of the diversifiable risk". 15 Stocks eliminates over 93%. The benefit of adding more stocks tails off very rapidly after even about ten stocks, which eliminates 90% of the diversifiable risk.
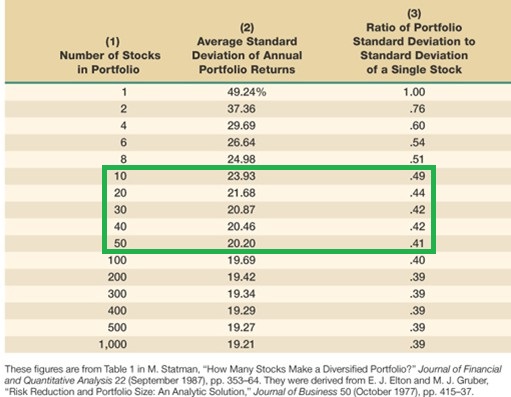
Tang's paper contains a table of researchers who have validated this result with empirical studies mainly of the US stock market. Most of the studies show the ideal number topping out at 30, though a couple go as high as 40. A similar Canadian study Diversification with Canadian Stocks: How much is enough? by Sean Cleary and David Copp in the 1999 Canadian Investment Review concludes that 30 to 50 stocks would have captured most (85-90%) of the diversification benefits during 1985 to 1997.
Caveat #1 - Diversification works effectively with low market risk
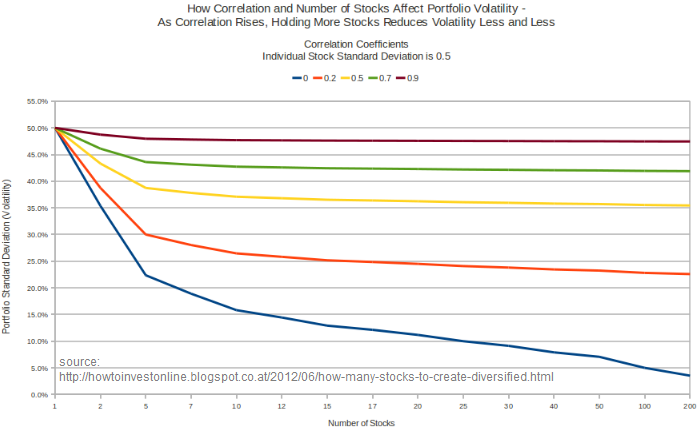
When inter-stock correlation (aka market risk) rises, holding more stocks does little to reduce overall portfolio volatility. Even when stocks have a relatively low overall average correlation of 0.4 what starts off as 50% standard deviation (volatility) for one stock can only be reduced to around 32% with 100 stocks. That's not even half the overall volatility gone. The chart below shows what happens with stock correlation numbers. The lower the correlation, the more the portfolio's volatility can be reduced. When correlation is high at 0.9 diversification has little effect: one stock with a 50% volatility can only be reduced to about 47.5% volatility in a 100-stock portfolio. With a more normal 0.5 correlation, the 100-stock portfolio reduces volatility to about 35.5%.
Bottom line: holding many stocks won't help much in a crisis when panic causes all stocks to fall in tandem.
Caveat #2 - Cost and effort go up with larger portfolios
The time to do research into companies, to track and assess on-going results and the transaction costs to keep the portfolio in balance can be a considerable burden.
One possible Investor Takeaway
Recognize that you will only be somewhat diversified. Indeed a primary objective will be not to be diversified but to be concentrated in a restricted number of stocks that you feel will do better. Legendary investor Warren Buffett puts it this way as quoted on StreetDirectory.com: "Diversification may preserve wealth, but concentration builds wealth." Nevertheless, that doesn't mean holding only one or two companies. Even Buffett's investment company Berkshire Hathaway owns dozens of companies and stocks.



